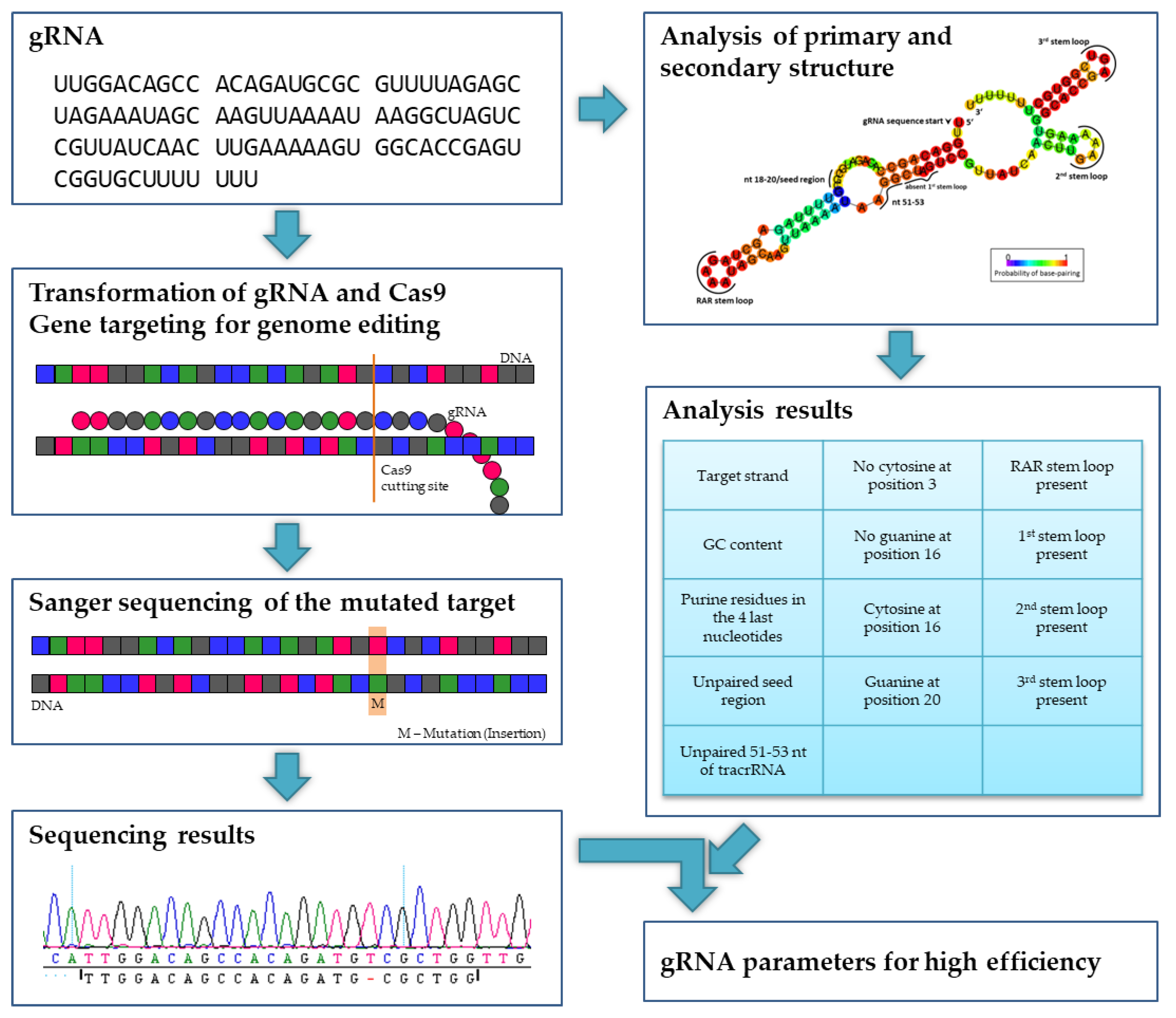
Wong et al further analyzed the dataset of Doench et al and reported that nucleotides at position 18– are the seed region of the gRNA This region and the nucleotides located at 51–53 should be unbound and accessible to form efficient gRNAs If the seed region would bind to position 51–53 of the gRNA, it would be nonfunctionalImportantly, the spacer region of the gRNA remains free to interact with target DNA Cas9 will only cleave a given locus if the gRNA spacer sequence shares sufficient homology with the target DNA Once the Cas9gRNA complex binds a putative DNA target, the seed sequence (810 bases at the 3′ end of the gRNA targeting sequence) will begin to anneal to the target DNACasOT is a genomewide Cas9/gRNA offtarget search toolThe CRISPR/Cas or Cas9/guide RNA system is a newly developed, easily engineered and efficient gene targeting toolIt has considerable offtarget effects in cultured human cells and in some organismsHowever, the Cas9/guide RNA target region is too short for existing alignment tools to fully and effectively identify potential off
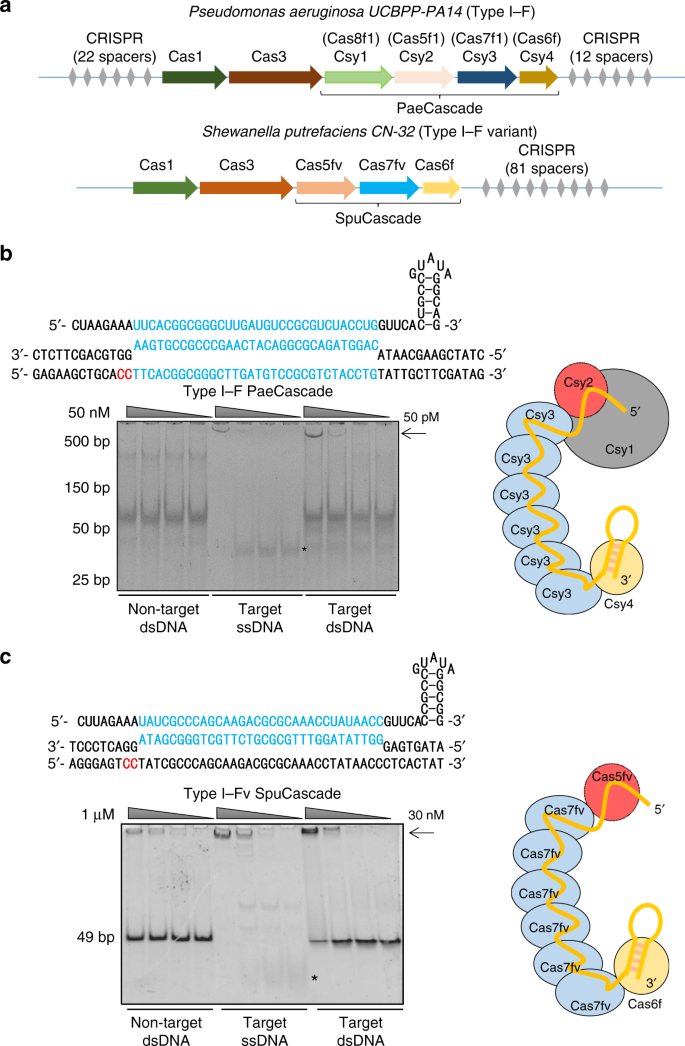
Repurposing Type I F Crispr Cas System As A Transcriptional Activation Tool In Human Cells Nature Communications
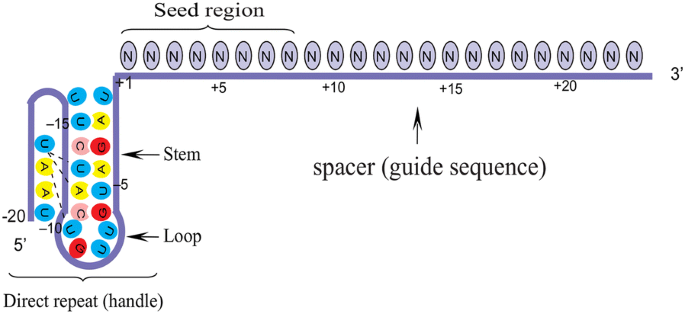
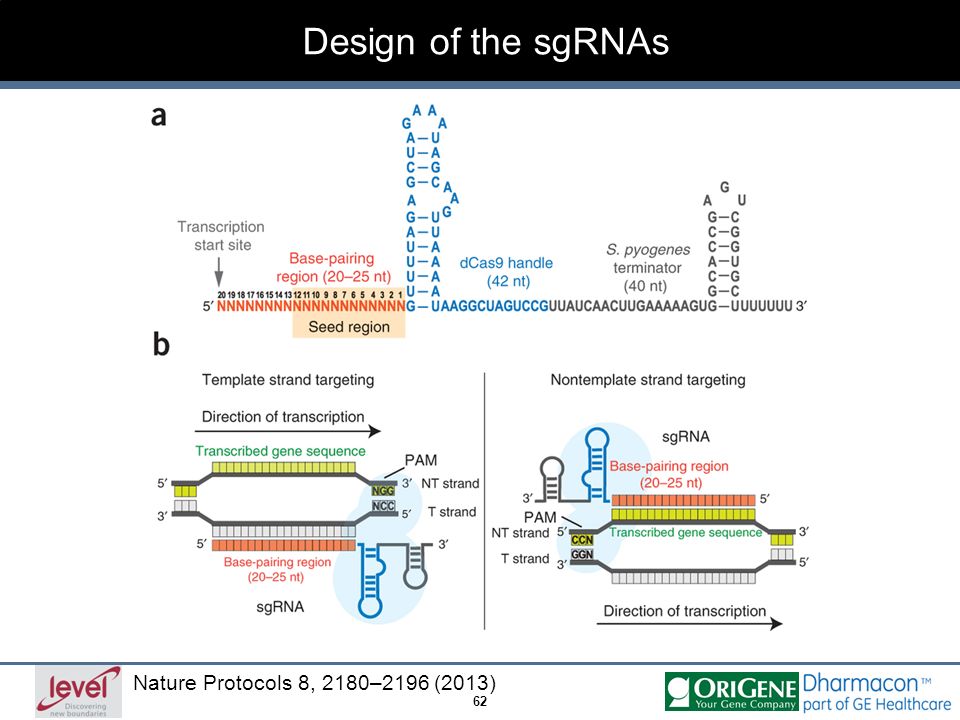
Grna seed region
Grna seed region-Once the PAM is recognized, the guide region of the gRNA undergoes seed nucleation to form an Aformlike helical RNADNA hybrid duplex Only once the RNA and DNA complete Rloop formation, also known as the zipped conformation, and structural rearrangement of the nuclease domains commence, can the endonuclease cut the DNA creating a DSB ( Jiang etCas9sgRNA RNPs can recut a given genomic target following HDR if the editing outcome does not involve alteration of the PAM or sgRNA seeding region in the protospacer sequence, such that the RNP complex can still bind to the genomic target




Addgene Crispr Guide
One consequence of the zipping model is that the gRNAprotospacer duplex can be divided into two functional domains Basepairing within the seed, or PAMproximal region (positions 110), contributes most strongly to targeting the Cas9RNP to specific sequencesSgRNA binding through multiple potential mechanisms The sequence of the seed region determines the frequency of a "seed NGG" in the genome, and controls the effective concentration of the Cas9sgRNA complex (Cas9 binding or sgRNA abundance and specificity)21,25 Meanwhile, Urich seeds are likely to result in decreased sgRNA abunThe seed sequence or seed region is a conserved heptametrical sequence which is mostly situated at positions 27 from the miRNA 5´end Even though base pairing of miRNA and its target mRNA does not match perfect, the "seed sequence" has to be perfectly complementary
SgRNA In vitro Transcrpition Kit () CRISPR/Cas9 System (Green) () CRISPR/Cas9 System (Red) () Mutation Detection KitIt is important for gRNA to interact initially with preedited mRNA and then its 5' region base pair with complementary mRNA The 3' end of gRNA contains oligo 'U' tail (525 nucleotides in length) which is a non encoded region but interacts and forms a stable complex with A and G rich regionsNucleotides 51–53 of the tracrRNA should be not paired to the seed region and be freely accessible, and there should be favorable nucleotides at several positions
B) mismatches within the PAMproximal 8–12 nucleotide seed region of the guide sequence reduce gRNA activity to a greater degree than mismatches outside the seed region;The PS1–gRNA seed region (22 nt) was predicted to pair with the template strand of OsMPK5, and would guide Cas9 to make DSB at a Kpn I site The PS2– and PS3–gRNA seeds region ( and 22 nt, respectively) were predicted to pair with the coding strand of OsMPK5, and PS3–gRNA would guide Cas9 to make DSB at a Sac I site (Figure 2B)CRISPRCas9 is a simple twocomponent system that allows researchers to precisely edit any sequence in the genome of an organism This is achieved by guide RNA, which recognizes the target sequence, and the CRISPRassociated endonuclease (Cas) that cuts the targeted sequence Researchers across the globe who are adopting this technology are bound to come across an




Addgene Crispr Guide




Setup Of Pmn Fkbp Cas9 And Pmn Grna Constructs A Cartoon Download Scientific Diagram
After exposure to cas9/gRNA, we PCR out the region of interest for 1224 individual colonies and sequence through the cut site We then calculate the ratio of mutation or insertion/deletion at the cut site (indels) to unmodified wildtype sequence (wildtype) to get indel frequence = indels/wildtype*100 (as a percentage)SgRNA 디자인 sgRNA 제작 및 효율 검증 sgRNA, Cas9 세포 내 도입 Mutation 확인 Indel Identification <Complete System>The genomic target region (purple indicator) is composed of bp that are homologous to the gRNA (white) and a PAM sequence (green indicator) The tail region (orange indicator) of the genomic target, which is most distal from the PAM motif, is more permissive of mismatches, while the 8–12 nt seed region (blue indicator) most proximal to the PAM is critical



Www Mdpi Com 1422 0067 22 4 1878 Pdf




Off Target Assessment Of Crispr Cas9 Guiding Rnas In Human Ips And Mouse Es Cells Tan 15 Genesis Wiley Online Library
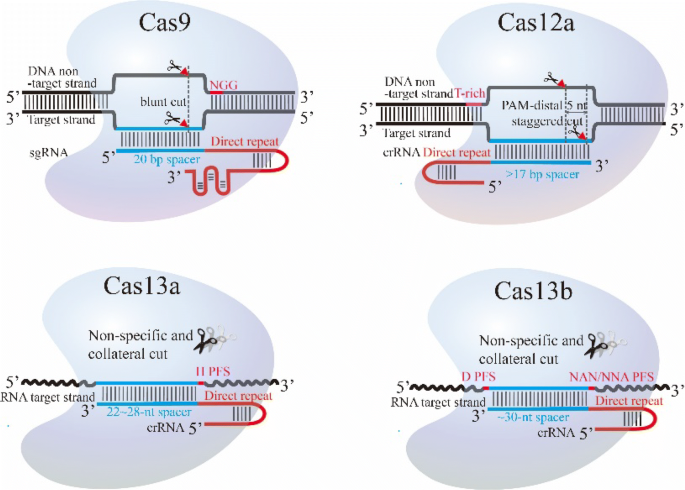
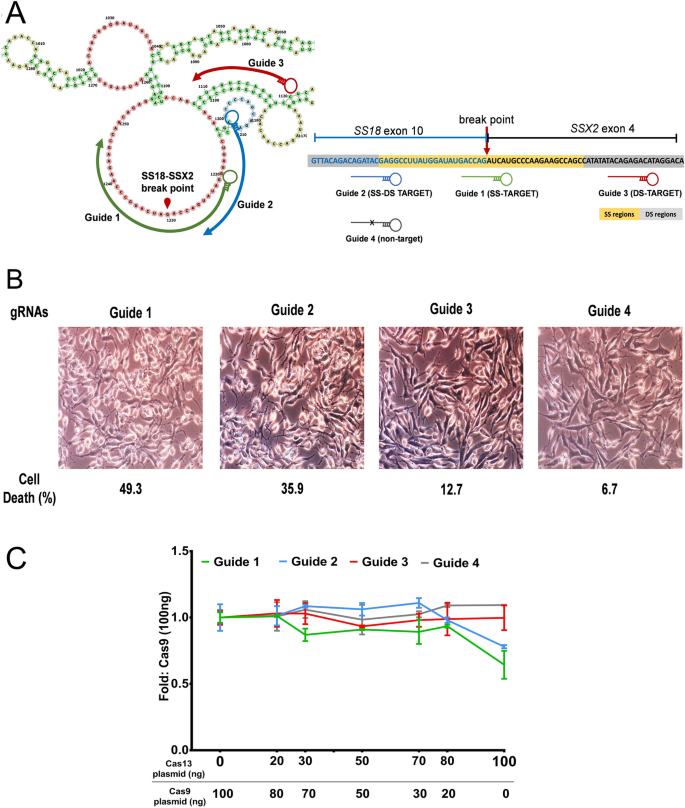
The presence of a single mismatch within the seed region of the guide sequence greatly reduced but did not abolish gRNA activity, whereas the presence of an additional mismatch, or the absence of a PAM, all but abolished gRNA activityUtilizing structureseq data for XIST transcript, we observed that gRNAs targeting the SS regions significantly induce transcript knockdown and cleavage than those targeting doublestranded (DS) regions Further, we identified the central seed region in the gRNA that upon targeting the SS regions efficiently facilitates Cas13 mediated cleavageThe target DNA sequence needs to be followed by a protospacer adjacent motif (PAM), typically NGG Cas9 is a DNA endonuclease with two active domains (red triangles) cleaving each of the two DNA strands three nucleotides upstream of the PAM The five nucleotides upstream of the PAM are defined as the seed region for target recognition



Pubs Rsc Org En Content Articlepdf Sc D0sce




A Cas9 Is Directed To A Specific Genomic Target By The First Nt Of Download Scientific Diagram
The guide RNA is a specific RNA sequence that recognizes the target DNA region of interest and directs the Cas nuclease there for editing The gRNA is made up of two parts crispr RNA (crRNA), a 17 nucleotide sequence complementary to the target DNA, and a tracr RNA, which serves as a binding scaffold for the Cas nuclease• Base pairing between the seed region of engineered gRNAs and the targeted sites in the OsMPK5 gene PS1gRNA was paired with the coding strand of OsMPK5 whereas PS2 and PS3 gRNA were paired with the template strand of OsMPK5 The predicted gRNACas9 cutting position was indicated with the scissor symbolThis option allows users to calculate scores based on a particular region of the input sequences, such as the seed region of the gRNA Note that if the input sequence is longer than bp without PAM or 23 bp with PAM, only the first nucleotides are analyzed Results Page




Crispr Plant




Sgrna Multiplexing Strategies A Rna Endonuclease Csy4 Recognizes A Download Scientific Diagram
We observed that during sgRNA cloning errors sometimes occur with sequences containing microhomology regions next to the junctions We have therefore developed an alternative, ligationfree method for the PCRcloning of sgRNAs into the pMZ379 plasmid, using two longer primers that each contain the complete nt sgRNA sequences, in opposite orientation,Offtargets are regions of gRNA that are highly homologous to the proposed ontarget regions Normally offtarget regions have up to six mismatches compared with ontarget sites18 CRISPR/Cas9 specificity mainly relies on the sgRNA seed Adv Sci , 7,CRISPR was originally employed to knock out target genes in various cell types and organisms, but modifications to various Cas enzymes have extended CRISPR to selectively activate/repress target genes, purify specific regions of DNA, image DNA in live cells, and precisely edit DNA and RNAThe sgRNAs can accommodate mismatches varying by as many as five nucleotides in the 5′ upstream region




Crispr Cas9 Abm Inc
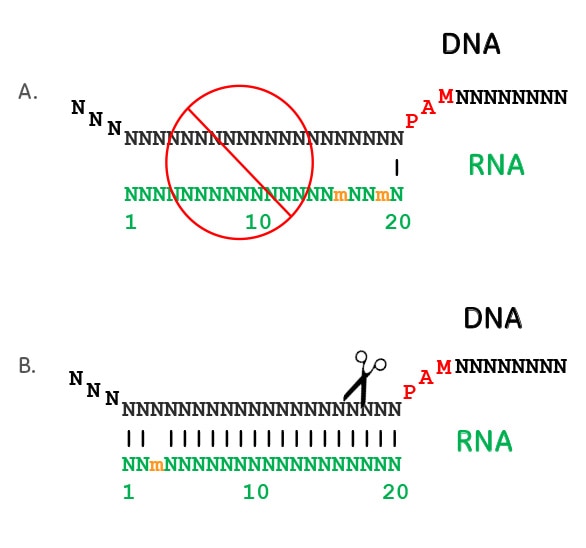



Crispr Cas9 Guide Rna Specificity
Collectively, recent structural and mechanistic studies provide not only a fundamental understanding of CRISPR–Cas9 mechanisms but also a framework for structurebased rational design aimed at improving CRISPR–Cas9 efficiency and minimizing offtarget effects for human health and therapeutics ( 25, 52 – 54, , 92 )Seed and nonseed sequences were further segmented into three parts region I (1–7 bp), region II (8–12 bp) and region III (13– bp) As shown in Figure 3A, the seed region contains regions I and II, while the nonseed region only contains region IIIFig 1 Overall structure of SpyCas9sgRNA binary complex (A) Domain organization of the type IIA Cas9 protein from S pyogenes (SpyCas9)(B) Secondary structure diagram of sgRNA bearing complementarity to a bp region λ1 DNAThe seed sequence is highlighted in beige Bars between nucleotide pairs represent canonical WatsonCrick base pairs;
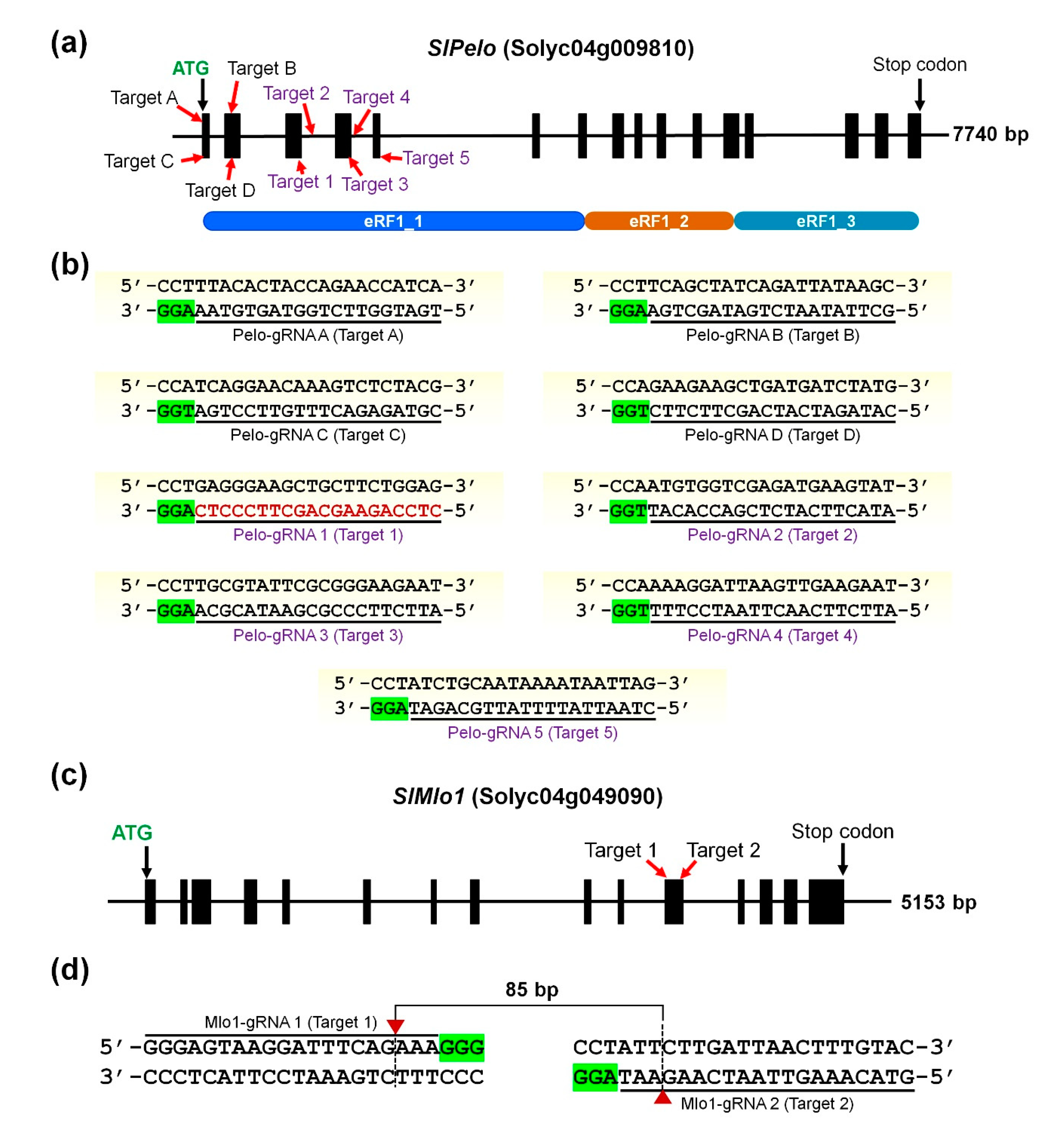



Ijms Free Full Text Crispr Cas9 Mediated Generation Of Pathogen Resistant Tomato Against Tomato Yellow Leaf Curl Virus And Powdery Mildew Html
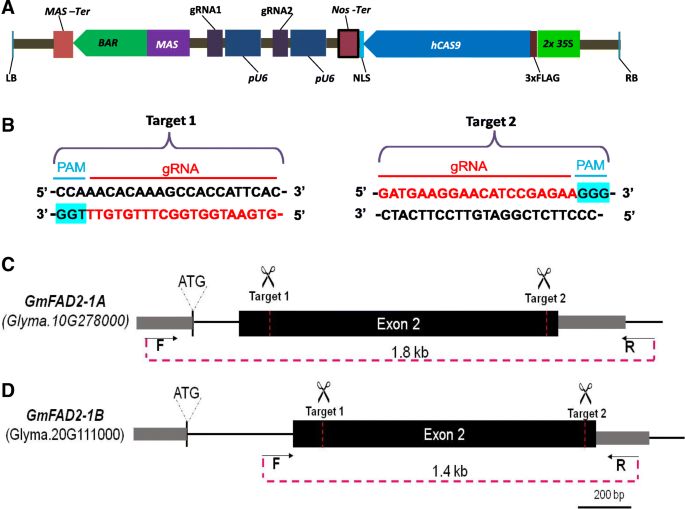



Demonstration Of Highly Efficient Dual Grna Crispr Cas9 Editing Of The Homeologous Gmfad2 1a And Gmfad2 1b Genes To Yield A High Oleic Low Linoleic And A Linolenic Acid Phenotype In Soybean Bmc Plant Biology
Unlike previous engineering of gRNA that generally focused on the RNA part only but neglected RNA–protein interactions, we aimed at the interactive sites between 2′OH of ribose in the seed region of gRNA and Cas9 protein and identified that modifications of 2′OH at specific sites could be utilized to regulate the Cas9 activityPerfect match to the 12nt seed region of the sgRNA and 4 mismatches in the outer segments M5_POT Perfect match to the 12nt seed region of the sgRNA and 5 mismatches in the outer segments Total_Noof_POT Total number of offtargets sites with perfect match to the 12nt seed region of the sgRNAGRNA sequence Genomic analysis results Seed region PAM AGG CGG AGG TCCTAAAC TCCTAAAC TCCTAAAC 1dentify target I loci where Cas9induced insertion or deletion (indel) formation will result in knockout of all isoforms of the gene, generally at 5´




Addgene Crispr Guide



Off Target Genome Editing Wikipedia
Since the seed region of gRNA is imperative for the activity, therefore, we calculated the GC content percentage of the PAM proximal seed region (1–12 nt) and the PAM distal region (13– nt) In the case of the PAM proximal seed region (1–12 nt), the GC content positively and significantly impacted the cleavage efficacy ( p value = 32E−02)Each gRNA candidate was compared with all known exon sequences in the genome Recent experimental studies revealed that the 3′ end seed region of the gRNA is more relevant to offtargeting than the nucleotides residing in the 5′ end Thus, a more stringent filter is applied to this PAMproximal seed regionWe obtained evidence for a relationship between the structure of gRNA and the e ciency of gene editing In particular, the GC content, purine residues in the gRNA end, and the free accessibility of the seed region seemed to be highly important for genome editing in poplars Based on our findings on nine di erent poplar genes,




Efficient Multiplex Biallelic Zebrafish Genome Editing Using A Crispr Nuclease System Pnas



Ijms Free Full Text Crispr Cas9 Mediated Generation Of Pathogen Resistant Tomato Against Tomato Yellow Leaf Curl Virus And Powdery Mildew Html
Full gRNAmRNA hybridization is triggered once the gRNA critical seed region (nt2nt4) binds to the target mRNA The fully hybridized structure isOf note, both motifs are located in the sgRNA "seed" region (the PAMproximal 10–12 bases of the targeting sequence) that is important forOur results are consistent with established models of gRNA specificity 27,28,29,30 in which a) the absence of a canonical PAM site (5′NGG3′) greatly reduces or abolishes gRNA activity;




Single Base Resolution Increasing The Specificity Of The Crispr Cas System In Gene Editing Molecular Therapy




Systematic Analysis Of Crispr Cas9 Mismatch Tolerance Reveals Low Levels Of Off Target Activity Sciencedirect
Exons 6 Filter out any overlapping sequences, if possible 7 Select the top 4 highestscoringFig 1 Focusing on the interaction between the seed region of gRNA and Cas9 protein (a) Interactive sites between the OH and the residues of Cas9 revealed by the crystal structure The numbering starts from the 50end of gRNA with a standard nt guide sequence (b) The guide sequence investigated for gene ASCL1 The seed region is highlightedThe sgRNA is tightly bound with the Cas9 protein The first nt of sgRNA (red) is base paired with the DNA target (orange) and the rest sgRNA nucleotides (green) have rich interactions with the




Sample Input File And Possible Off Target Types In The Casot Download Scientific Diagram




Addgene Crispr Guide
The seed sequence in the gRNA contributes greatly to the specificity of Ago RNP interactions with target substrates The canonical seed region of all eAgos and some pAgos is composed of the second to eighth nts of the gRNA and has an Aform helical conformation in the Ago RNP complex (18 ⇓⇓⇓⇓ – 23)Each mutant sgRNA was tested for its activity in directing Cas9 cleavage of naked DNA or nucleosome substrates, following a 30min incubation A number of single sgRNA mismatches had significant effects on cleavage of the naked DNA substrate, particularly mismatches in the sgRNA seed region (Fig 2, B and C), consistent with previous studiesSeveral features were mentioned to enhance gRNA effectiveness 17,18 the last three base pairs of the gRNA (seed region) should be unpaired and freely accessible ;




Crispr Cas Systems In Genome Editing Methodologies And Tools For Sgrna Design Off Target Evaluation And Strategies To Mitigate Off Target Effects Manghwar Advanced Science Wiley Online Library




Generation And Validation Of Homozygous Fluorescent Knock In Cells Using Crispr Cas9 Genome Editing Abstract Europe Pmc
It has been shown that as few as four mismatches in the PAM‐distal end hinder cleavage but not binding 36, 37 CRISPR/Cas9 specificity mainly relies on the sgRNA seed sequence within 10–12 bp directly 5′ of the NGG PAM‐proximal region 38 When the sgRNA sequence recognizes partial mismatches outside the seed sequence instead of on‐target sites,Three guide RNAs (gRNAs) with a –22nt seed region were designed to pair with distinct rice genomic sites which are followed by the protospaceradjacent motif (PAM) The engineered gRNAs were shown to direct the Cas9 nucleasePAM (seed region) are especially important for target site recognition In many cases, offtarget mutations happen at sites where the gRNA seed region has no mismatches but the nonseed region does 3, 15 To knock out a specific region in the genome, such offtarget effects should be avoided Reducing such risk is espe



Frontiers Crispr Cas9 Genome Editing Technology A Valuable Tool For Understanding Plant Cell Wall Biosynthesis And Function Plant Science




Target Dependent Nickase Activities Of Crispr Cas Nucleases Cpf1 And Cas9 Semantic Scholar




Repurposing Type I F Crispr Cas System As A Transcriptional Activation Tool In Human Cells Nature Communications



2




Engineered Rna Interacting Crispr Guide Rnas For Genetic Sensing And Diagnostics The Crispr Journal




Crispr Cas Systems In Genome Editing Methodologies And Tools For Sgrna Design Off Target Evaluation And Strategies To Mitigate Off Target Effects Manghwar Advanced Science Wiley Online Library



Dr Gaetan Burgio Md Phd Auf Twitter Interesting This Paper Published Today In Naturemicrobiol Shows That Crispr Cas9 Or Cas12a Cpf1 Can Display An Inherent Potent Nicking Activity In Yeast This Nicking




Schematics Of Cas9n Grna Target Sequence Specific Fluorescent Download Scientific Diagram



Crispr Cpf1 Proteins Structure Function And Implications For Genome Editing Cell Bioscience Full Text




Crispr Plant




Rna Guided Genome Editing In Plants Using A Crispr Cas System Sciencedirect



Academic Oup Com G3journal Article Pdf 9 1 287 G3journal0287 Pdf




Wu Crispr Characteristics Of Functional Guide Rnas For The Crispr Cas9 System Biorxiv




Binding Of Central Seed Region In Grna Crucial For Cas13 Mediated Download Scientific Diagram



Class 2 Crispr Cas An Expanding Biotechnology Toolbox For And Beyond Genome Editing Cell Bioscience Full Text



Www Cell Com Molecular Plant Pdf S1674 52 16 4 Pdf
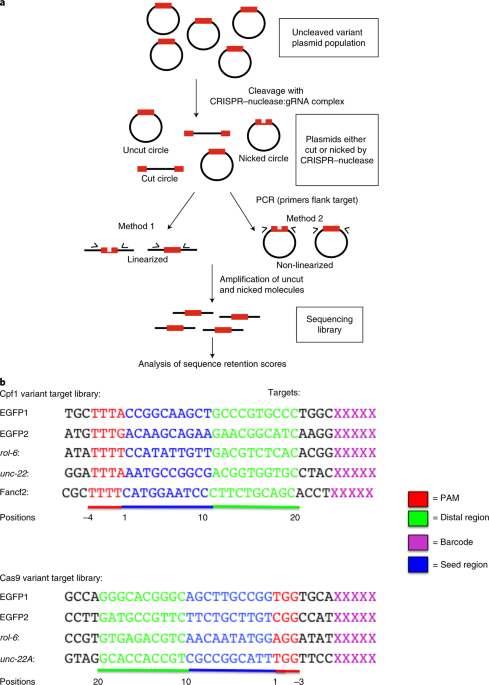



Target Dependent Nickase Activities Of The Crispr Cas Nucleases Cpf1 And Cas9 Nature Microbiology




Dual Sgrna Based Targeted Deletion Of Large Genomic Regions
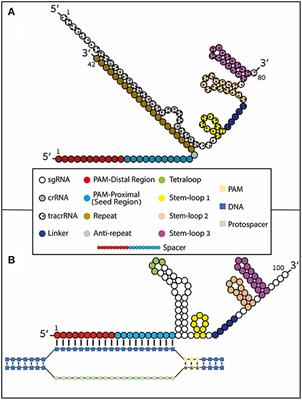



Frontiers Using Synthetically Engineered Guide Rnas To Enhance Crispr Genome Editing Systems In Mammalian Cells Genome Editing




Off Target Effects In Crispr Cas9 Mediated Genome Engineering Sciencedirect




Tricks And Trends In Crispr Cas9 Based Genome Editing And Use Of Bioinformatics Tools For Improving On Target Efficiency Sciencedirect
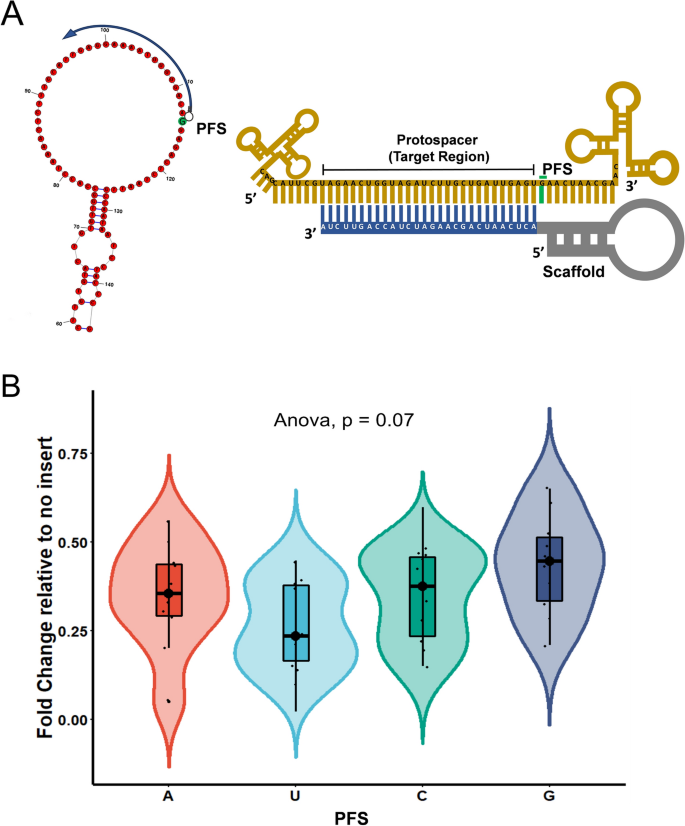



Structure Based Design Of Grna For Cas13 Scientific Reports




Structure Based Design Of Grna For Cas13 Scientific Reports
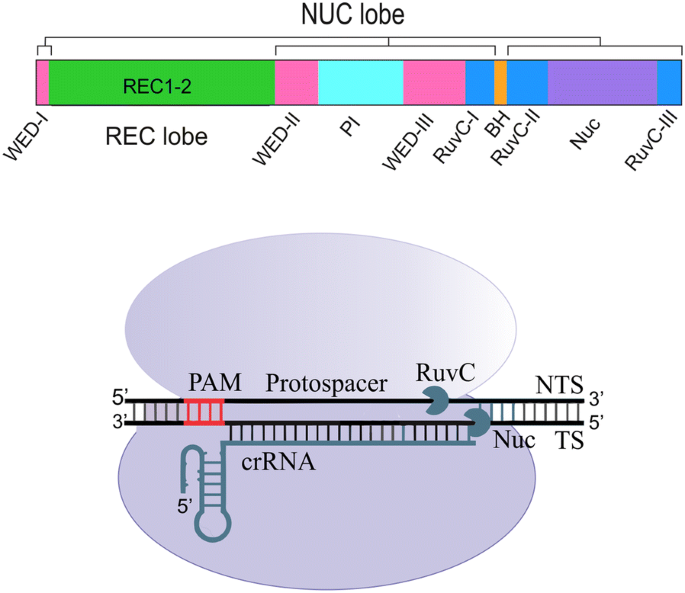



Crispr Cpf1 Proteins Structure Function And Implications For Genome Editing Cell Bioscience Full Text
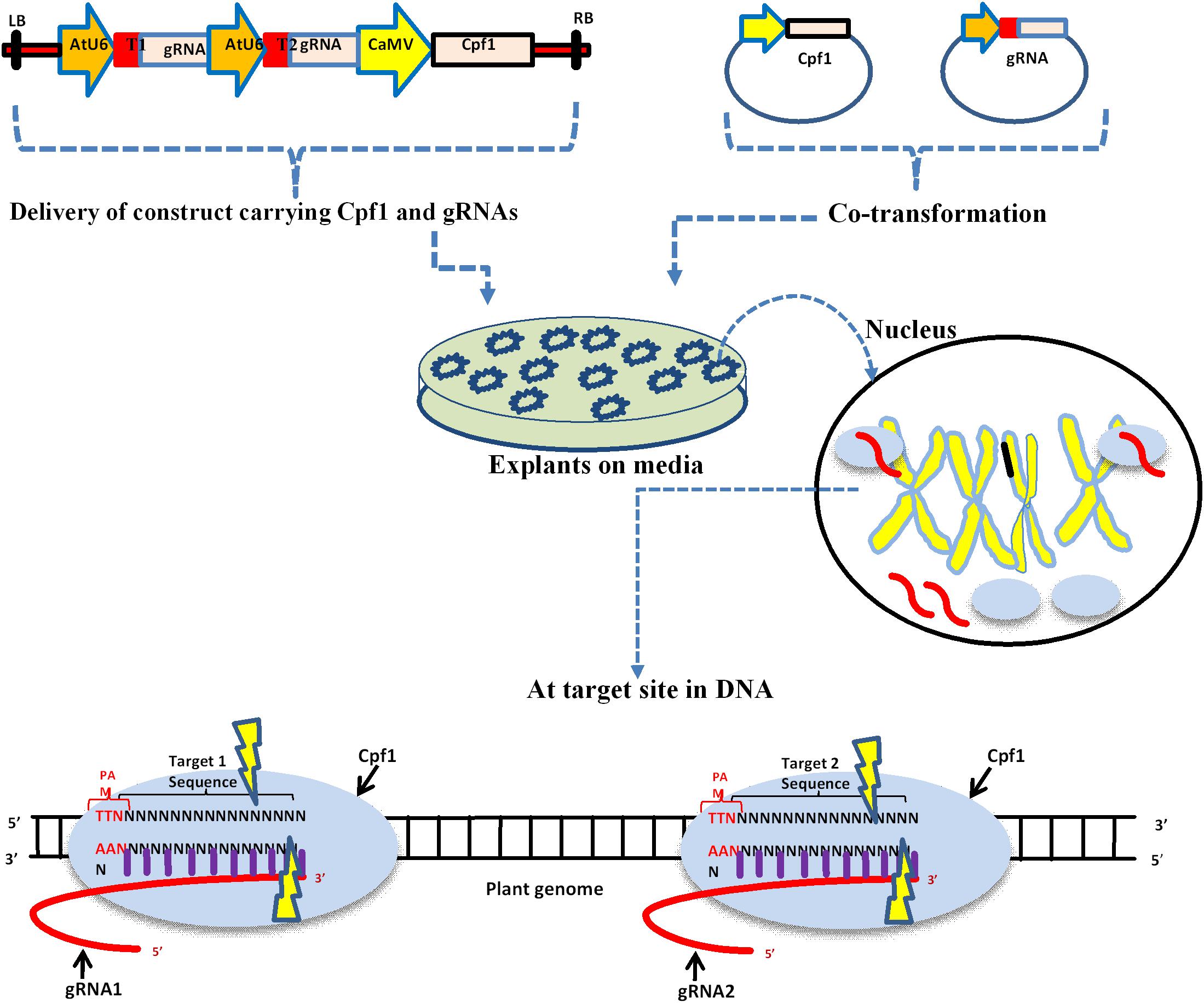



Frontiers The Rise Of The Crispr Cpf1 System For Efficient Genome Editing In Plants Plant Science



Www Mdpi Com 1422 0067 22 4 1878 Pdf
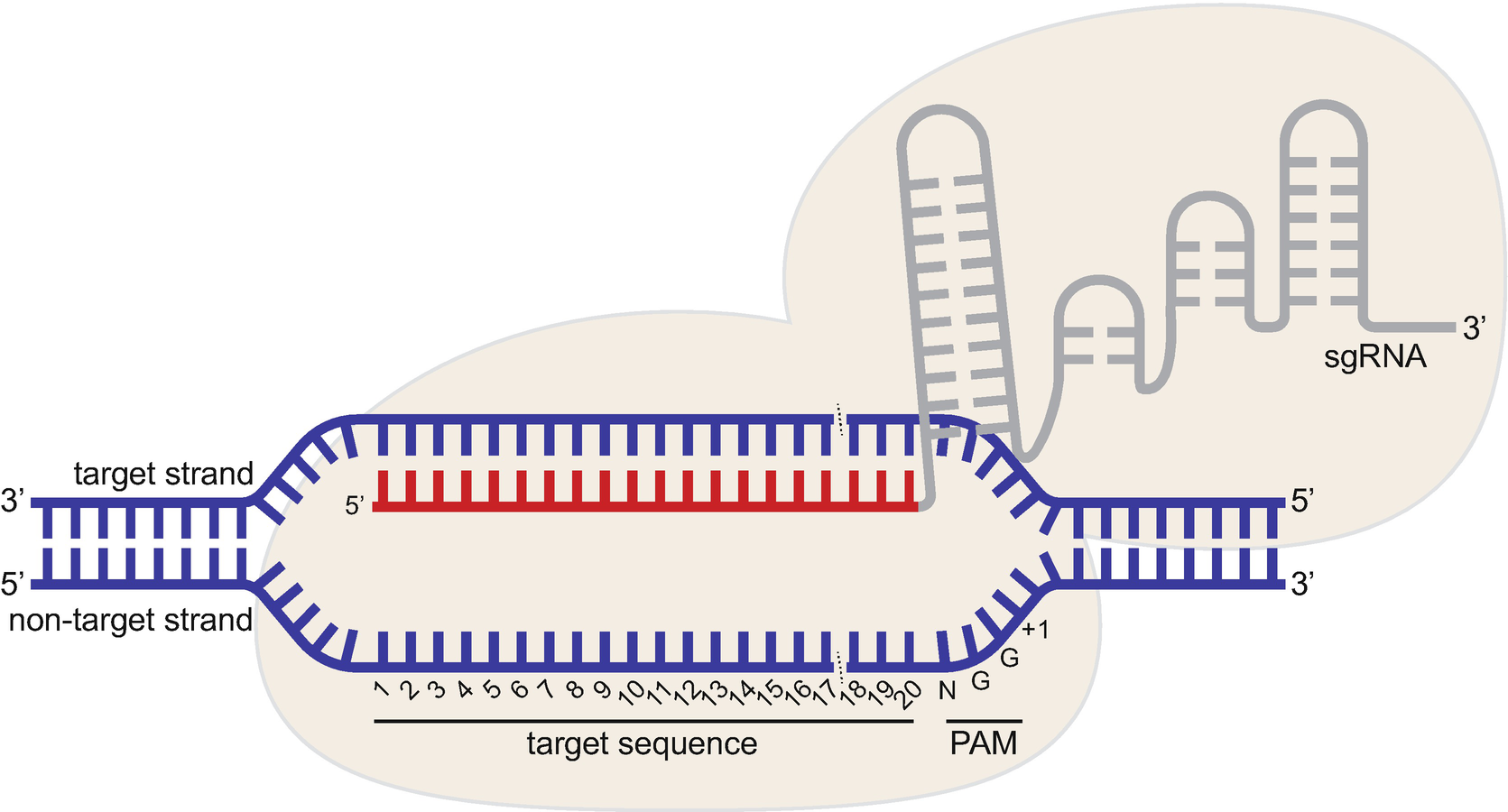



Crispr Cas9 Guide Rna Design Rules For Predicting Activity Springerlink




Sgrna Sequence Motifs Blocking Efficient Crispr Cas9 Mediated Gene Editing Sciencedirect




Programmable Rna Recognition Using A Crispr Associated Argonaute Biorxiv




Quantification Of Cas9 Binding And Cleavage Across Diverse Guide Sequences Maps Landscapes Of Target Engagement Science Advances




Schematic Illustration Of Cas9 Grna Genome Editing A Sgrna Mediated Download Scientific Diagram




Rna Guided Genome Editing In Plants Using A Crispr Cas System Molecular Plant



Structure Based Design Of Grna For Cas13 Scientific Reports




Efficient Multiplex Biallelic Zebrafish Genome Editing Using A Crispr Nuclease System Abstract Europe Pmc



Engineering Virginia Edu Sites Default Files Common Departments Computer Science Files Fast Searching For Potential Grna Off Target Sites For Crispr Cas9 Using Automata Processing Pdf




A Model For Cas9 Target Binding And Cleavage A In The Unbound State Download Scientific Diagram




Genomic Sequences Bound By Cas9 Grna Comprehensive List Of Sequences Download Scientific Diagram




Crispr Cas9 Gene Drives In Genetically Variable And Nonrandomly Mating Wild Populations Science Advances



Grna Validation For Wheat Genome Editing With The Crispr Cas9 System Bmc Biotechnology Full Text




Crispr Plant




Type Ii Crispr Formulations Grnas Contain 4 Loop Structures Download Scientific Diagram



1




Crispr Cas9 Abm Inc




Cas9 Cuts And Consequences Detecting Predicting And Mitigating Crispr Cas9 On And Off Target Damage Newman Bioessays Wiley Online Library




Crispr Dt Designing Grnas For The Crispr Cpf1 System With Improved Target Efficiency And Specificity Biorxiv
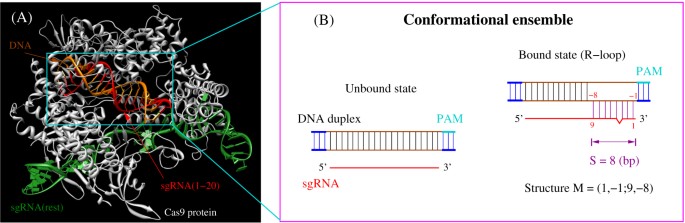



Crispr Cas9 Cleavage Efficiency Correlates Strongly With Target Sgrna Folding Stability From Physical Mechanism To Off Target Assessment Scientific Reports



1



Plos One Sgrnacas9 A Software Package For Designing Crispr Sgrna And Evaluating Potential Off Target Cleavage Sites
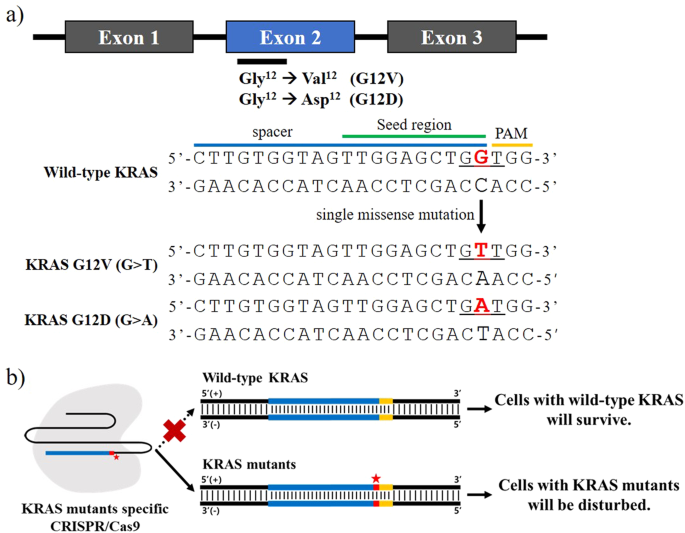



Selective Targeting Of Kras Oncogenic Alleles By Crispr Cas9 Inhibits Proliferation Of Cancer Cells Scientific Reports




Modification Of Cas9 Grna And Pam Key To Further Regulate Genome Editing And Its Applications Sciencedirect




Addgene Crispr Guide



Field Application Scientist Level Biotechnology Inc Ppt Video Online Download
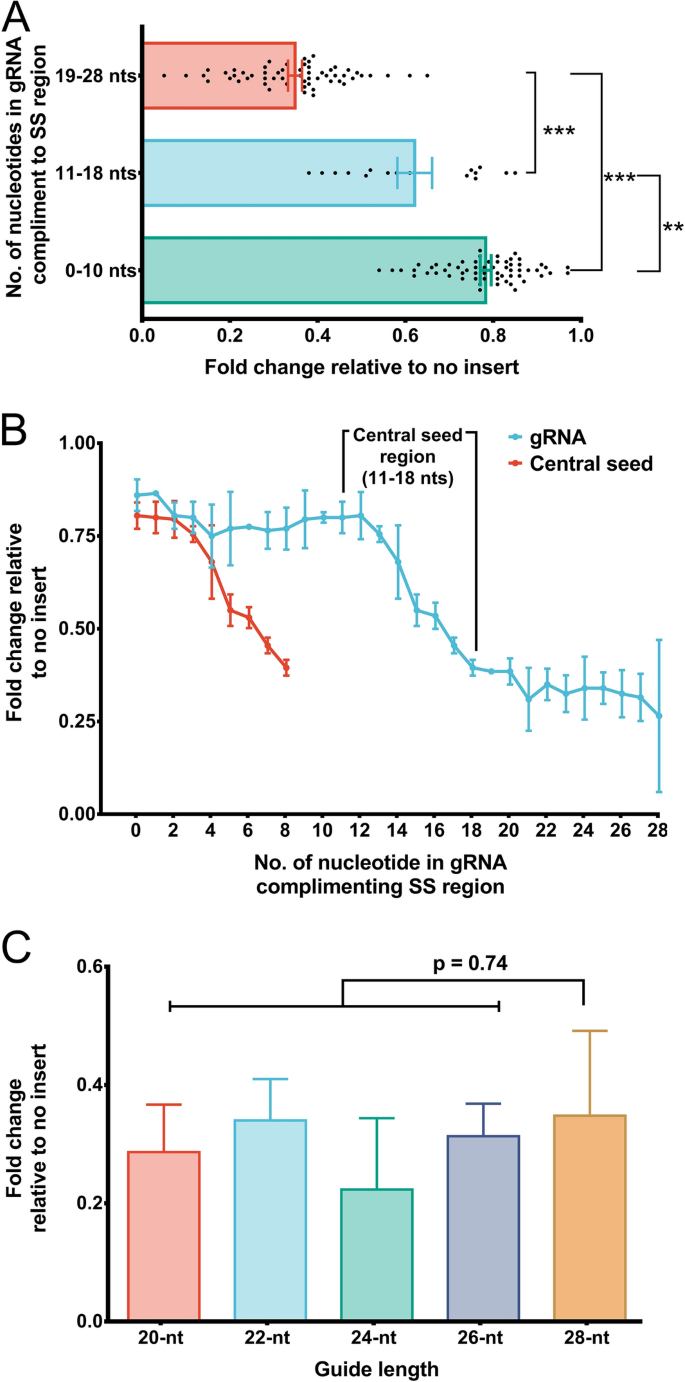



Structure Based Design Of Grna For Cas13 Scientific Reports



Academic Oup Com G3journal Article Pdf 9 1 287 G3journal0287 Pdf




Addgene Crispr Guide
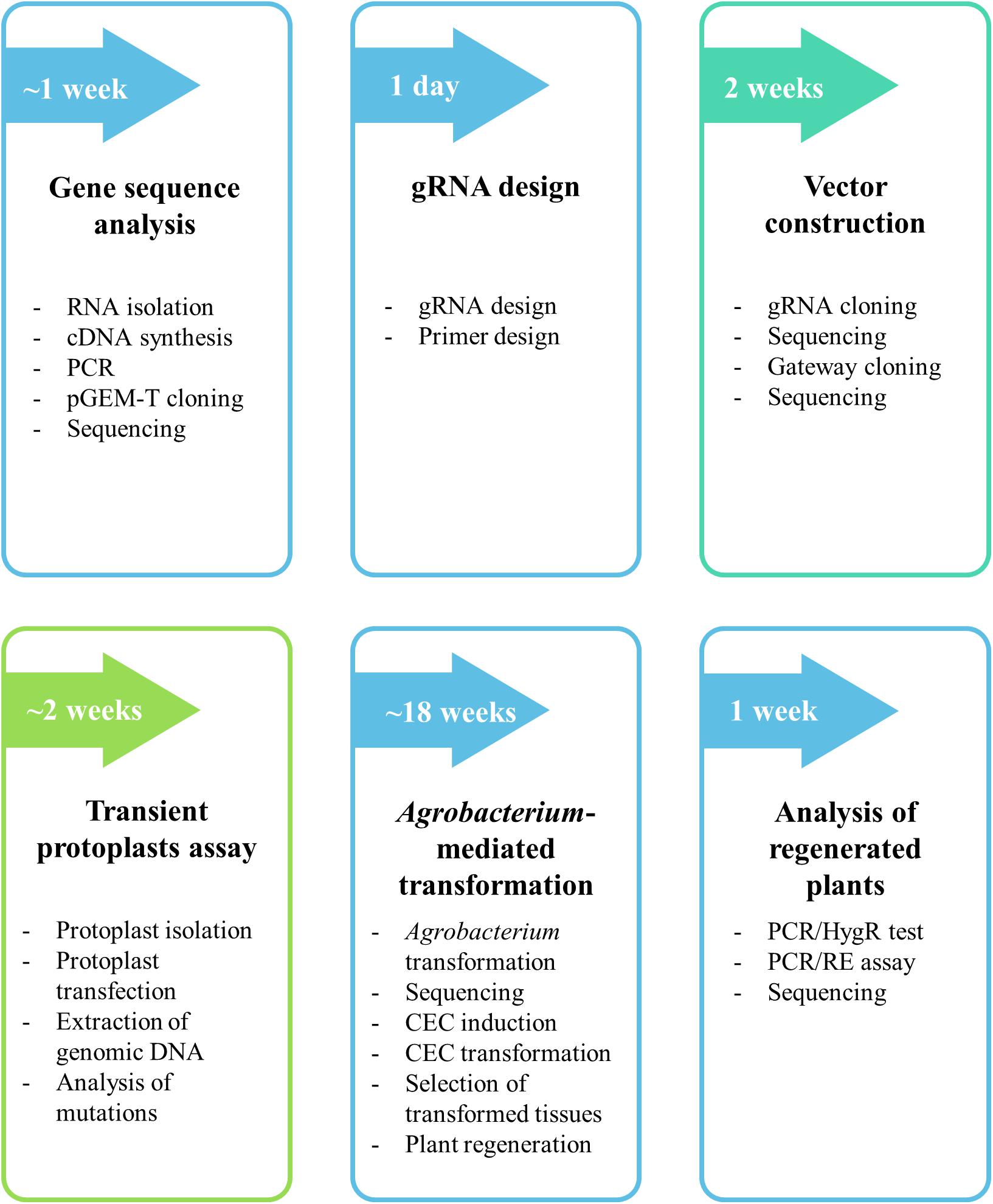



Frontiers A Crispr Cas9 Based Mutagenesis Protocol For Brachypodium Distachyon And Its Allopolyploid Relative Brachypodium Hybridum Plant Science



D Nb Info 34



Academic Oup Com Pcp Article Pdf 59 8 1608 Pcy079 Pdf



1



Academic Oup Com G3journal Article Pdf 9 1 287 G3journal0287 Pdf




Genomic Sequences Bound By Cas9 Grna Comprehensive List Of Sequences Download Scientific Diagram



A Cas9 Is Directed To A Specific Genomic Target By The First Nt Of Download Scientific Diagram



Plos One Sgrnacas9 A Software Package For Designing Crispr Sgrna And Evaluating Potential Off Target Cleavage Sites




Addgene Crispr Guide




Esqsd Goena Dm




Off Target Genome Editing Wikipedia
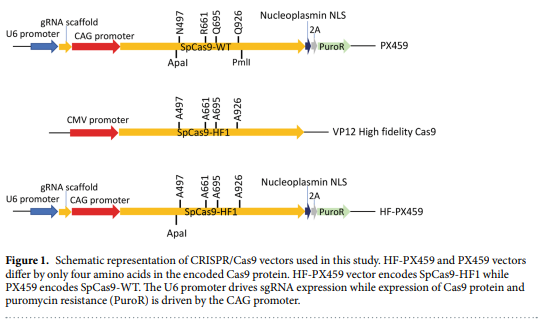



High Fidelity Crispr Cas9 Increases Precise Monoallelic And Biallelic Editing Events In Primordial Germ Cells Engormix




Crispr Cas9 Abm Inc




Target Dependent Nickase Activities Of The Crispr Cas Nucleases Cpf1 And Cas9 Abstract Europe Pmc
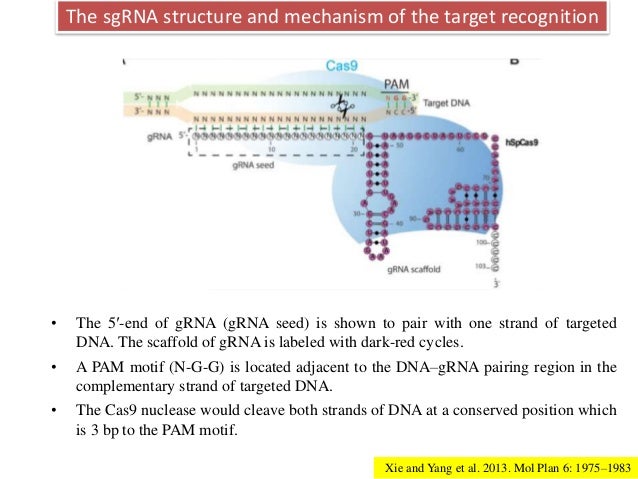



Genome Editing



Journals Asm Org Doi Pdf 10 1128 Msphere 17




Systematic Analysis Of Crispr Cas9 Mismatch Tolerance Reveals Low Levels Of Off Target Activity Sciencedirect
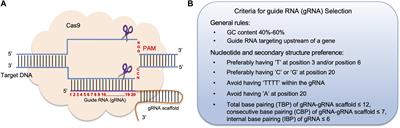



Frontiers Crispr Cas9 Genome Editing Technology A Valuable Tool For Understanding Plant Cell Wall Biosynthesis And Function Plant Science
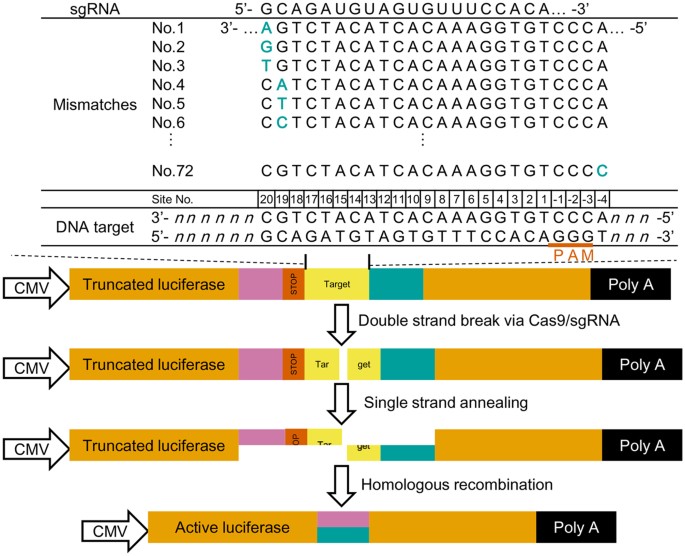



Profiling Single Guide Rna Specificity Reveals A Mismatch Sensitive Core Sequence Scientific Reports
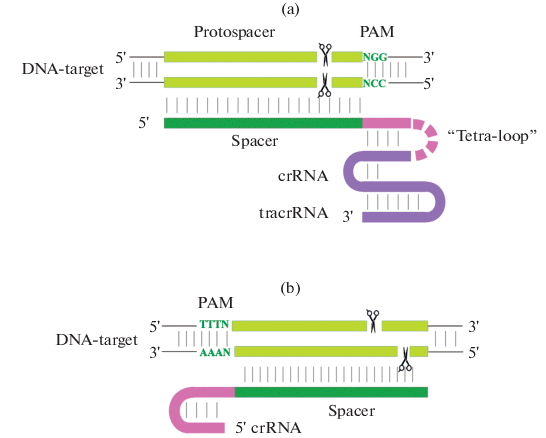



Design Of Guide Rna For Crispr Cas Plant Genome Editing Springerlink



1




Rfxcas13d Bsj Grna Discriminates Circrnas From Mrnas A Schematic Of Download Scientific Diagram



Ijms Free Full Text Evaluating The Efficiency Of Grnas In Crispr Cas9 Mediated Genome Editing In Poplars Html




Rna Guided Genome Editing In Plants Using A Crispr Cas System Sciencedirect
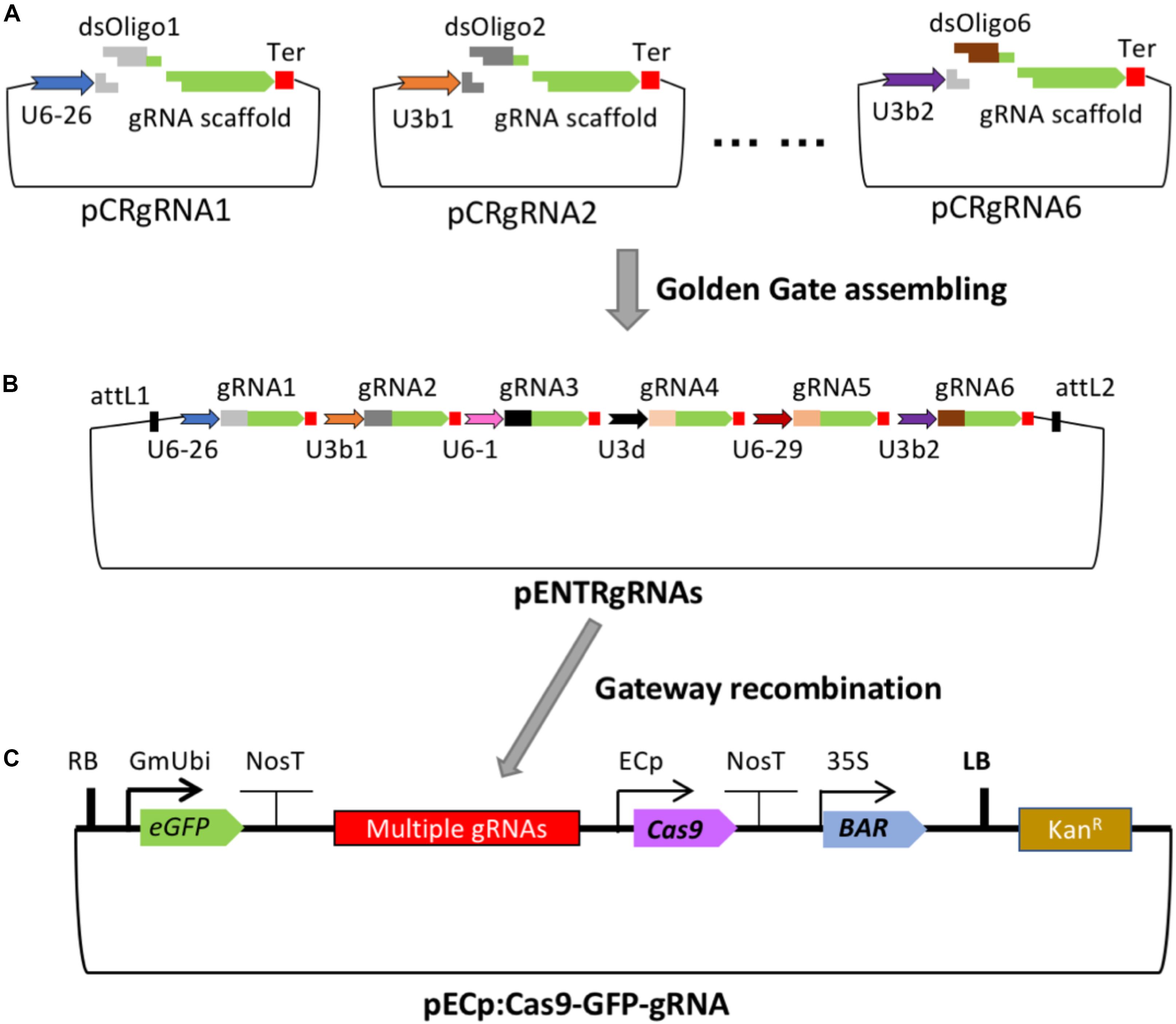



Frontiers Crispr Cas9 Based Gene Editing Using Egg Cell Specific Promoters In Arabidopsis And Soybean Plant Science




The Crispr Cas Revolution Continues From Efficient Gene Editing For Crop Breeding To Plant Synthetic Biology Kumlehn 18 Journal Of Integrative Plant Biology Wiley Online Library



Document For Crispr Ge



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿